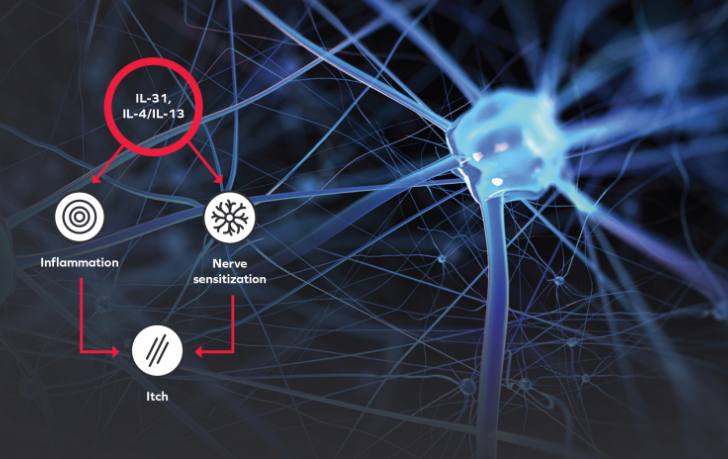
Drivers of Atopic Dermatitis
Itch, inflammation, and skin barrier disruption are 3 pillars of AD. The neuroimmune communication between sensory neurons, keratinocytes, and inflammatory mediators contribute to AD pathophysiology.1-5
Learn More
- Steinhoff M, Ahmad F, Pandey A, et al. Neuroimmune communication regulating pruritus in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149(6):1875-1898. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.03.010
- Dubin C, Del Duca E, Guttman-Yassky E. The IL-4, IL-13 and IL-31 pathways in atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021;17(8):835-852.doi:10.1080/1744666X.2021.194096
- Yosipovitch G, Berger T, Fassett MS. Neuroimmune interactions in chronic itch of atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34(2):239-250. doi:10.1111/jdv.15973
- Kim J, Kim BE, Leung DYM. Pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis: clinical implications. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019;40(2):84-92. doi:10.2500/aap.2019.40.4202
- Renert-Yuval Y, Guttman-Yassky E. New treatments for atopic dermatitis targeting beyond IL-4/IL-13 cytokines. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019;124(1):28-35. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2019.10.005
References



